Monetary policy is a crucial tool used by governments and central banks to influence economic conditions, and a Fed rate cut is one of the most powerful levers the U.S. Federal Reserve can pull to control the economy. But what exactly is a Fed rate cut, and how does it work? More importantly, how does it affect you as a consumer or a business owner, and what are the global implications, especially for countries like India?
This article will break down the concept of a Fed rate cut, its purpose, the risks involved, and how it impacts various sectors of the economy. Understanding these effects can help you make more informed financial decisions in response to shifts in monetary policy.
Table of Contents
What is a Fed Rate Cut?
A Fed rate cut refers to the lowering of the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. This rate serves as a benchmark for many other interest rates in the economy, including those on mortgages, credit cards, and business loans. When the Federal Reserve cuts this rate, it is essentially making it cheaper for banks to borrow money, and they, in turn, pass these lower costs onto consumers and businesses.
The Federal Reserve sets the federal funds rate as part of its broader monetary policy to manage inflation, employment, and overall economic growth. A rate cut typically signals that the Fed is trying to stimulate the economy by making borrowing cheaper, thereby encouraging spending and investment.
Why Does the Fed Cut Interest Rates?
1. To Stimulate Economic Growth
One of the primary reasons for a Fed rate cut is to boost economic growth, especially during periods of economic slowdown or recession. Lower interest rates make it cheaper for businesses and consumers to borrow money, which can increase spending and investment. In turn, this stimulates economic activity and can help to reduce unemployment.
For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed slashed rates to near zero in an effort to revive the struggling economy. A similar move was made during the COVID-19 pandemic, when the global economy was hit hard by lockdowns and reduced consumer spending.
2. To Manage Inflation
The Fed may also cut rates to manage inflation, though this is less common. In general, the Fed raises interest rates to control inflation by making borrowing more expensive, which can cool off an overheating economy. However, during times of low inflation or deflation, a rate cut can help to prevent prices from falling too quickly, which can be damaging to the economy.
3. To Address Global Economic Conditions
The U.S. economy is deeply intertwined with the global economy, and a Fed rate cut can have far-reaching effects beyond the U.S. borders. For example, during periods of global economic uncertainty, such as trade wars or geopolitical tensions, the Fed may cut rates to maintain financial stability and prevent a global downturn.
How Does the Fed Rate Cut Affect the Economy?
The impact of a Fed rate cut is felt across multiple sectors of the economy, affecting everyone from individual consumers to large corporations. Here’s a breakdown of how a Fed rate cut can influence different areas:
Consumer Spending
One of the most direct effects of a Fed rate cut is on consumer spending. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, which can encourage people to take out loans for big-ticket items such as homes, cars, and appliances. This increase in spending helps to drive economic growth.
For example, if you’re in the market for a new home, a Fed rate cut could lower the interest rate on your mortgage, making homeownership more affordable. Lower interest rates also reduce the cost of financing other types of debt, such as credit cards and personal loans.
Business Investment
Businesses also benefit from lower borrowing costs when the Fed cuts rates. Companies may take advantage of lower interest rates to finance new projects, expand their operations, or hire more employees. This increase in business investment can create jobs and stimulate further economic growth.
For instance, a manufacturing company might use borrowed funds to invest in new equipment, while a tech startup could use a loan to scale its operations. In both cases, lower borrowing costs make these investments more feasible and attractive.
Stock Markets and Bonds
The stock market often reacts positively to a Fed rate cut because lower interest rates can boost corporate profits by reducing borrowing costs. Investors may also shift their money from bonds to stocks because bonds tend to offer lower returns in a low-interest-rate environment.
However, a Fed rate cut isn’t always good news for bondholders. When the Fed cuts rates, the yield on new bonds typically falls, which means bond investors receive lower returns. For those holding existing bonds, the value of their bonds may rise, but future income from new bond purchases will be reduced.
Real Estate Market
The real estate market often sees a significant impact from Fed rate cuts, particularly in the housing sector. Lower interest rates can make mortgages more affordable, which can spur home buying and increase housing demand. This, in turn, can drive up home prices, creating opportunities for both buyers and sellers.
During periods of low interest rates, homeowners with existing mortgages may also consider refinancing to lock in a lower rate, potentially saving thousands of dollars in interest payments over the life of the loan.
The Risks of Overusing Fed Rate Cuts
While a Fed rate cut can provide a much-needed boost to the economy, it is not without risks. Over-reliance on rate cuts can lead to unintended consequences, including:
Inflation
If the Fed cuts rates too aggressively or keeps them low for too long, it can lead to inflation. When borrowing is cheap and spending increases, prices may rise too quickly, eroding the purchasing power of consumers. If inflation becomes too high, the Fed may be forced to raise rates quickly to prevent the economy from overheating, which could slow growth.
Asset Bubbles
Prolonged periods of low interest rates can also contribute to the formation of asset bubbles. When borrowing is cheap, investors may take on excessive risk, driving up the prices of assets like real estate, stocks, or cryptocurrencies. If these asset prices rise too far, too fast, it can create a bubble that eventually bursts, leading to significant financial losses and economic instability.
Currency Devaluation
Lower interest rates can lead to a weaker currency, as foreign investors seek higher returns elsewhere. A weaker U.S. dollar can increase the cost of imports, contributing to inflation. However, it can also make U.S. exports more competitive by reducing the cost of American goods abroad.
How the Fed Rate Cut Impacts India
The U.S. Federal Reserve’s decisions don’t just affect the U.S. economy—they have ripple effects across the world, including in India. Here are some ways a Fed rate cut can impact the Indian economy:
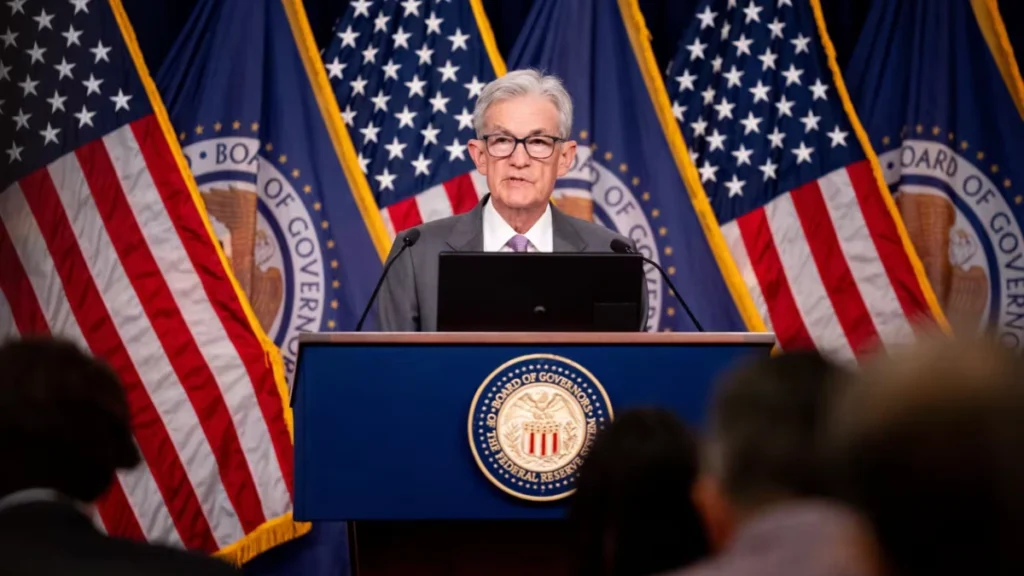

Capital Flows
When the Fed cuts interest rates, it can lead to increased capital flows into emerging markets like India. Investors seeking higher returns may move their capital from U.S. bonds to Indian stocks, bonds, or other investments, boosting liquidity in Indian markets.
However, this influx of foreign capital can also lead to increased volatility, as investors may pull their funds out just as quickly if economic conditions change.
Exchange Rates
A Fed rate cut can also influence the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Indian rupee. When U.S. interest rates fall, the value of the dollar may decrease relative to other currencies, including the rupee. A stronger rupee can make Indian exports more expensive, potentially reducing demand for Indian goods in international markets. On the other hand, a stronger rupee can make imports cheaper, benefiting Indian consumers and businesses that rely on imported goods and services.
Impact on Inflation
Fed rate cuts can affect global commodity prices, such as oil, which India imports in large quantities. Lower global interest rates can reduce the cost of borrowing for commodity producers, leading to lower prices for goods like oil. This can help India control inflation and reduce import costs, especially in sectors heavily reliant on foreign goods.
Key Indicators to Watch When the Fed Cuts Rates
When the Fed cuts rates, it’s essential to keep an eye on several economic indicators to gauge the effectiveness and potential risks of the policy:
- Inflation Rates – Rate cuts are often aimed at stimulating the economy, but if inflation rises too quickly, the Fed may need to reverse course.
- Unemployment Data – Rate cuts are designed to spur job creation. A falling unemployment rate is a positive sign that the economy is responding to the policy.
- Consumer Confidence – Higher consumer confidence indicates that people are more willing to spend and borrow, which can lead to economic growth.
Final Thoughts: Preparing for a Fed Rate Cut
A Fed rate cut can have far-reaching effects on both the U.S. economy and the global financial system. As a consumer, business owner, or investor, it’s crucial to understand how these policy changes can affect your financial decisions. By staying informed and keeping an eye on key economic indicators, you can make the most of opportunities presented by lower interest rates while avoiding potential risks.
In conclusion, while a Fed rate cut can provide a powerful boost to the economy, it is not a cure-all for economic challenges. It must be used in conjunction with other fiscal and monetary policies to ensure long-term economic stability. By understanding the nuances of rate cuts and their broader implications, you can better navigate the economic landscape and make more informed financial decisions.
By addressing this topic with depth, clarity, and relevance, this article aims to help you understand the complexities behind Fed rate cuts, their impacts on the economy, and what it all means for you as a consumer, investor, or business owner.
7. Fed rate cut impact on gold
A Fed rate cut tends to boost the price of gold. This is because lower interest rates reduce the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets like gold. Additionally, when rates are cut, the dollar often weakens, making gold more attractive to investors as a safe-haven asset. Historically, gold prices rise in response to lower interest rates.
8. Fed interest rate decision today
The Fed interest rate decision today can be found by looking at the official announcement from the Federal Reserve after the FOMC meeting. These decisions are based on current economic data, including inflation, employment, and growth. News outlets such as CNBC and The Wall Street Journal provide real-time updates on Fed decisions, which can range from keeping rates steady to cutting or raising them depending on economic conditions.